Traversing The DOM - Nodes
Alright, so we looked at some important properties of the DOM that allow us to work with related elements. However, the DOM has more than just element nodes. In fact, there are 12 different types of nodes.
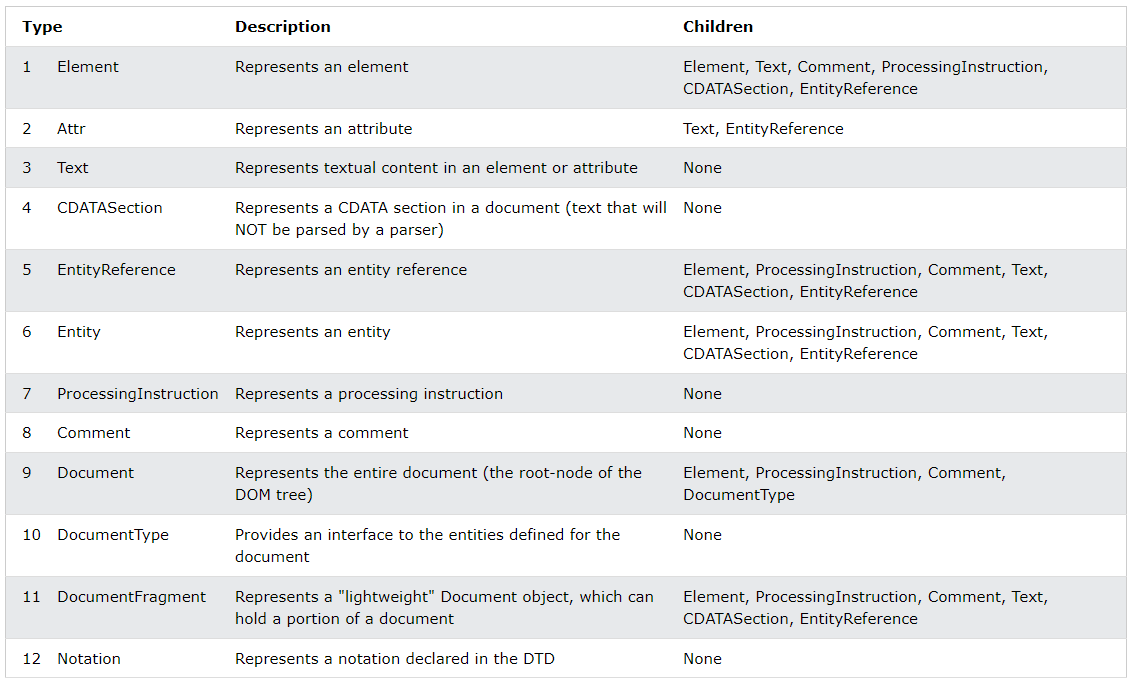 Table from W3Schools.com
Table from W3Schools.com
We don't really need to focus on most of these, but they're good to know.
Properties That Work With Nodes
The properties that we looked at in the last video were to work with related elements. However, there are other properties that we can use to access other types of nodes.
I would say for the most part, you will use the properties that we looked at in the last video, but you should know these as well.
We are going to use the same HTML structure as in the last video:
<div class="parent">
<!-- Children -->
<div class="child">Child 1</div>
<div class="child">Child 2</div>
<div class="child">Child 3</div>
</div>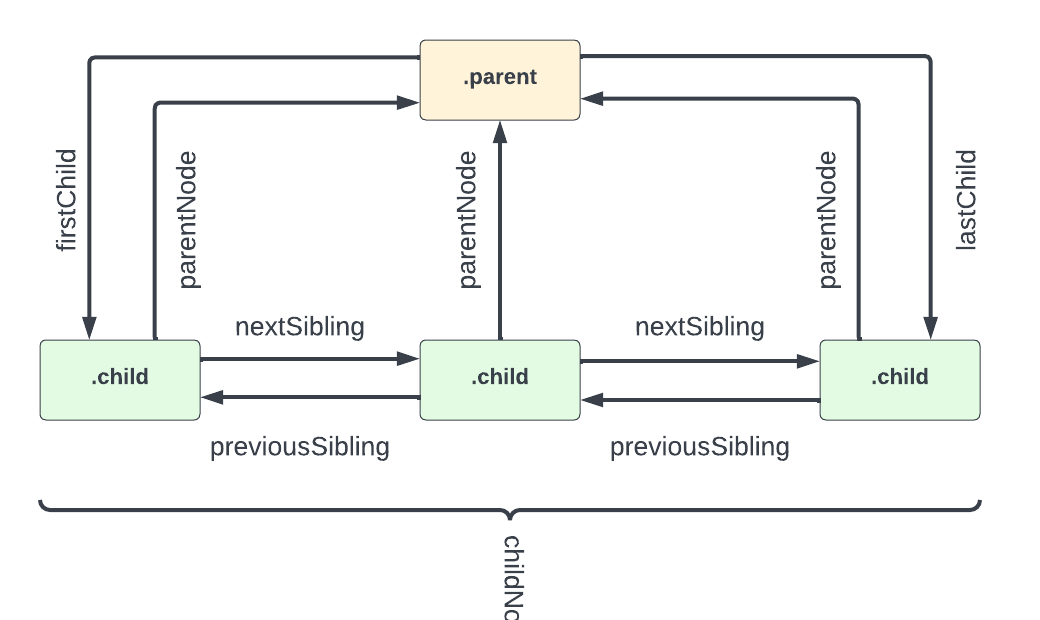
Child Nodes
childNodes
This method, does exactly what it says, it gets all of the child nodes of an element. This includes text nodes and comment nodes.
const parent = document.querySelector(".parent");
console.log(parent.childNodes);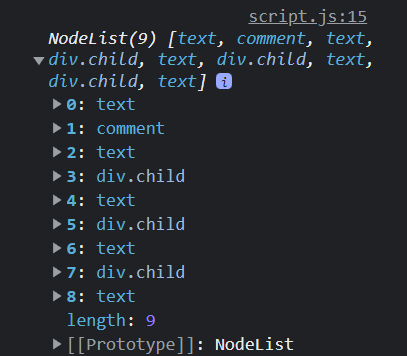
As you can see, we get a NodeList of 9 items. I want to go over what each of these items are...
- 0: White space is a
text node. Since the first line of HTML within the parentdiv(the comment) is on the next line, that line break is considered atext node. If I were to move the comment on to the same line as the parentdiv, then thetext nodewould be removed. I know, it's weird. - 1: The
commentnode. Comments are considered nodes as well. - 2: Another
text node. This is the line break between the comment and the first childdiv. - 3: The first child
div. - 4: Another
text node. This is the line break between the first childdivand the second childdiv. - 5: The second child
div. - 6: Another
text node. This is the line break between the second childdivand the third childdiv. - 7: The third child
div. - 8: Another
text node. This is the line break between the third childdivand the closingdivtag.
We can also access the nodes like this:
console.log(parent.childNodes[3]);
// <div class="child">Child 1</div>
// Get the node name
console.log(parent.childNodes[3].nodeName);
// 'DIV'
console.log(parent.childNodes[2].nodeName);
// '#text'
// Edit the first div
parent.childNodes[3].style.color = "red";The reason I used the index 3 is because 0, 1 and 2 are text and comment nodes. 3 is where the first element node is.
firstChild and lastChild
Just like we have firstElementChild and lastElementChild, we have firstChild and lastChild. the difference is that these two do not work only with element nodes.
// Get the first child node
output = parent.firstChild;
// #text
// Get the last child node
output = parent.lastChild;
// #text
To edit the value of a text node, we can use the nodeValue property.
parent.firstChild.nodeValue = "Hello";This will actually put the text of 'Hello' into the nodeValue, textContent, data and wholeText properties.
Parent Nodes
parentNode
In many ways, parentNode is very similar to parentElement. We can use it to do the same type of tasks.
To get the parent node of an element:
const child = document.querySelector(".child");
console.log(child.parentNode);
// <div class="parent">
The parent of an element will always be and element, document or documentFragment node type.
We looked at document.documentElement a few videos back. If we look at the parent node for that, it is a #document node
console.log(document.documentElement.parentNode);
// #document
We can edit the parent node/element, just like we could using the parentElement property.
child.parentNode.style.border = "1px solid #ccc";
child.parentNode.style.padding = "10px";If you want to get the parent document node of any element, you can use the ownerDocument property.
console.log(child.ownerDocument);
// #document
Sibling Nodes
nextSibling and previousSibling
Very similar to nextElementSibling and previousElementSibling, we have nextSibling and previousSibling.
const secondItem = document.querySelector(".child:nth-child(2)");
// Get next sibling
console.log(secondItem.nextSibling);
// #text
// Get previous sibling
console.log(secondItem.previousSibling);
// #text